Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS), also known as Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that impacts multiple body systems. It is characterised by distinctive facial features, cardiovascular issues, intellectual disability, and a unique personality profile. The condition is lifelong and occurs in approximately 1 in 20,000 to 1 in 7,500 births.

Overview
Signs and Symptoms
Physical Characteristics
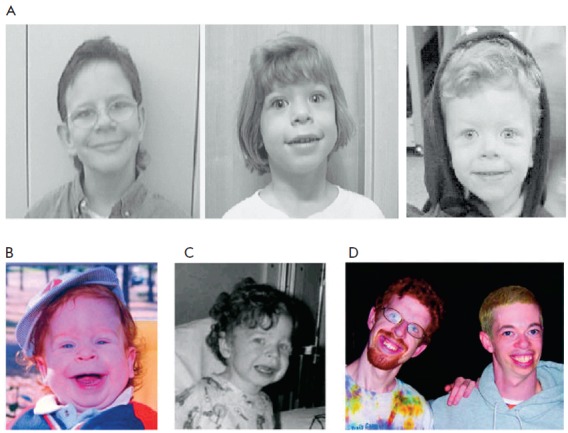
Individuals with WS often exhibit distinctive facial features, including a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Dental irregularities, such as widely spaced teeth and defective enamel, are common. Cardiovascular issues, particularly supravalvular aortic stenosis, are frequently observed. Other physical symptoms include gastrointestinal problems, hypercalcaemia, and reduced muscle tone.
Nervous System
WS affects the brain, resulting in abnormalities in the cerebellum, right parietal lobe, and left frontal cortical regions. This manifests as difficulties in visual-spatial tasks, fine motor coordination, and behavioural timing. People with WS often have a heightened ability in verbal communication but face challenges in tasks requiring spatial construction and orientation.
Developmental Delays
Developmental delays are evident early on, including low birth weight and failure to thrive. Language development is often delayed, with the first words appearing as late as three years old. Motor skill development, such as walking and coordination, is also delayed. These delays persist and sometimes worsen into adolescence and adulthood.
Social and Psychological Traits
Individuals with WS are highly sociable and exhibit little social inhibition. They often have a "cocktail party" personality, characterised by hyperverbal and friendly behaviour. Despite this, they frequently experience social isolation and loneliness. WS is associated with higher anxiety levels, phobias, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Cognitive abilities typically range from mild to moderate intellectual disability, with a mean IQ around 69.32.
Cause
Williams syndrome is caused by a microdeletion on chromosome 7q11.23, resulting in the loss of approximately 27 genes. Key genes affected include CLIP2, ELN, GTF2I, GTF2IRD1, and LIMK1. The deletion occurs randomly during the formation of egg or sperm cells. The haploinsufficiency of these genes leads to various symptoms, such as cardiovascular issues and cognitive disabilities.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of WS begins with the recognition of physical and physiological symptoms, such as distinctive facial features and cardiovascular problems. Confirmation is achieved through genetic testing, either via micro-array analysis or fluorescent in situ hybridisation (FISH). These tests identify the deletion of the elastin gene on chromosome 7, which is present in about 98-99% of WS cases.
Treatment
There is no cure for Williams syndrome, but various treatments can manage symptoms. These include dietary adjustments to manage hypercalcaemia, physical therapy for joint stiffness, and developmental and speech therapy. Cardiovascular issues are treated on an individual basis, often requiring surgical intervention. Annual cardiology evaluations and other regular health assessments are recommended by the American Academy of Paediatrics.
Behavioural treatments focus on improving social skills and managing phobias through cognitive-behavioural therapy. Music therapy has shown promise due to the strong affinity and aptitude for music observed in individuals with WS.
Epidemiology
Historically, WS was thought to occur in 1 in 20,000 live births, but recent studies suggest a prevalence closer to 1 in 7,500. The syndrome may have been underdiagnosed in the past, particularly in individuals lacking the characteristic facial features or those with higher intelligence levels.
History
Williams syndrome was first described in 1961 by J.C.P. Williams. Subsequent research in the 1960s and 1970s expanded understanding of its cardiovascular and behavioural symptoms. The syndrome's full name, Williams-Beuren syndrome, reflects the contributions of both Williams and German physician A.J. Beuren.
Society and Culture
The term "elfin" has been historically used to describe the facial features of individuals with WS. However, this terminology is now discouraged. Notable individuals with WS include Gabrielle Marion-Rivard, a Canadian actress and singer, and Jeremy Vest, a member of the How's Your News? team featured in a US TV series and film.
Self-assessment MCQs (single best answer)
What is the prevalence of Williams syndrome in births?
Which gene deletion is primarily responsible for Williams syndrome?
Which facial feature is NOT commonly associated with Williams syndrome?
What kind of cardiovascular issue is frequently observed in individuals with Williams syndrome?
What is the mean IQ range typically observed in individuals with Williams syndrome?
Which of the following is a common behavioural trait in individuals with Williams syndrome?
What is the primary method used to confirm a diagnosis of Williams syndrome?
Which therapy has shown promise due to the strong affinity for music in individuals with Williams syndrome?
Who first described Williams syndrome?
Which cognitive-behavioural aspect is often a focus in the treatment of individuals with Williams syndrome?
Dentaljuce
Dentaljuce provides Enhanced Continuing Professional Development (CPD) with GDC-approved Certificates for dental professionals worldwide.
Founded in 2009 by the award-winning Masters team from the School of Dentistry at the University of Birmingham, Dentaljuce has established itself as the leading platform for online CPD.
With over 100 high-quality online courses available for a single annual membership fee, Dentaljuce offers comprehensive e-learning designed for busy dental professionals.
The courses cover a complete range of topics, from clinical skills to patient communication, and are suitable for dentists, nurses, hygienists, therapists, students, and practice managers.
Dentaljuce features Dr. Aiden, a dentally trained AI-powered personal tutor available 24/7 to assist with queries and provide guidance through complex topics, enhancing the learning experience.
Check out our range of courses, or sign up now!


